Problem Statement Overview
To protect your company’s sensitive data, you must first find it and then classify it as either sensitive or non-sensitive data - after all, you cannot secure the unknown. Originally cybersecurity was a very straightforward process; first, secure the network edge or perimeter and then secure the layers in an inward progression. Data security, while considered important, was often the last area to receive budget allocation. As data privacy laws and regulations became more common, companies began to realize the value of their data and how bad of a risk a data breach could be. Companies shifted their focus towards a more granular level of data security, including finding where all their data resides, classifying it, and providing the right level of protection for it. But the solution became increasingly difficult, as data began to grow at increasingly faster rates throughout their company’s environment, creating challenges to even locate the data. Then the shift towards the cloud, multicloud, and hybrid environments exponentially made what was already a huge undertaking to find the data even more difficult.
Questions Your Peers Are Asking
- How do we put effective data security governance in place?
- How do we operationalize data classification?
- How do organizations anonymize data to address privacy issues?
- What approaches, techniques, and products should we use to encrypt and protect data on-premises and in the cloud?
Source: Gartner: Security of Applications and Data Primer for 2023
Published 14 February 2023 - ID G00779062
Today, companies have data located everywhere; in one or more clouds, on-premises, in hybrid environments, and in multiple data formats and data types - both structured and unstructured. The sheer volume of data often includes sensitive and highly confidential things, like PII, financial information, intellectual property, customer information, etc., and this data must be located, classified, and protected from unauthorized access. One of the best ways to secure data is to use cryptography to encrypt or tokenize it, depending on the ultimate data security objective, but of course, you must locate it first.
Strong cryptography is a fundamental approach to protecting the data, but it still requires companies to have careful access control policies in place based on an entity’s (person, machine, and/or application) identity and its specific role. To prevent business disruptions, all the encryption keys that enable data access must remain easily accessible, but at the same time, the encryption keys must be stored securely, separate from the data storage (Schrems-II regulation example). A solution to these challenges and risks is now available through the partnership between Fortanix and Imperva.
Imperva Data Security Fabric (DSF)
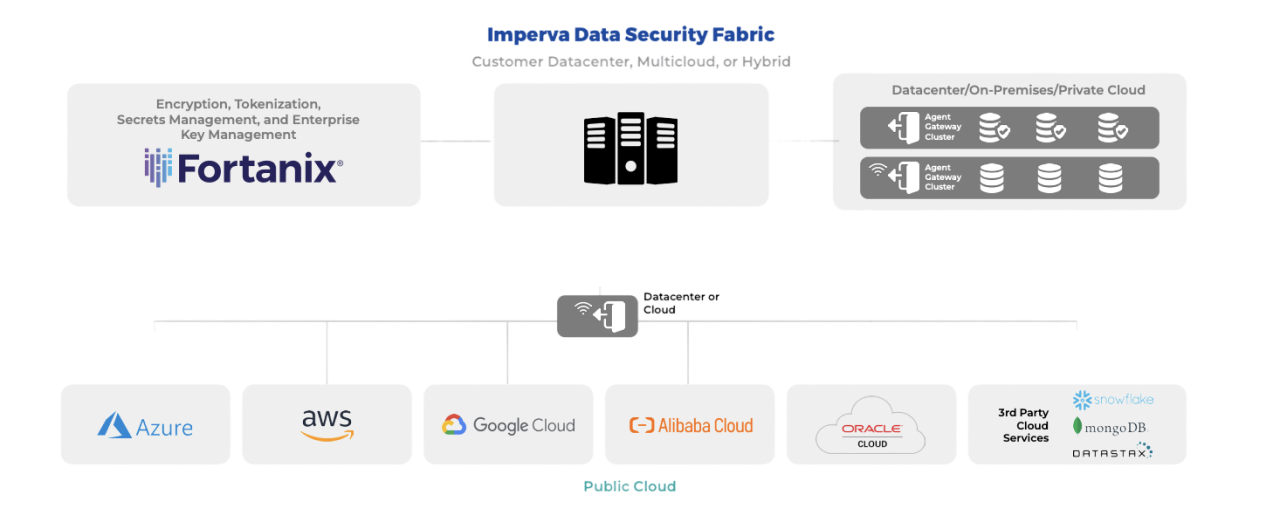
The award-winning Imperva Data Security Fabric (DSF) discovers, classifies, and secures all high-value data across file systems and data repositories.
Imperva Data Security Fabric (DSF) is a data-centric solution that enables security and compliance teams to quickly and easily secure sensitive data no matter where it resides with an integrated, proactive approach to visibility and predictive analytics.
Imperva’s Data Security Fabric solution simplifies data governance, security, and workflow management for sensitive data (structured, unstructured, and semi-structured) across multicloud and hybrid environments. This integrated solution helps organizations demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and maintain a strong data security posture through automated processes, audit analysis, and customizable reports. In addition, the Data Security Fabric solution accelerates incident responses, and forensic investigations with centralized management, prioritization of context-aware security alerts, and advanced analytics.solution.
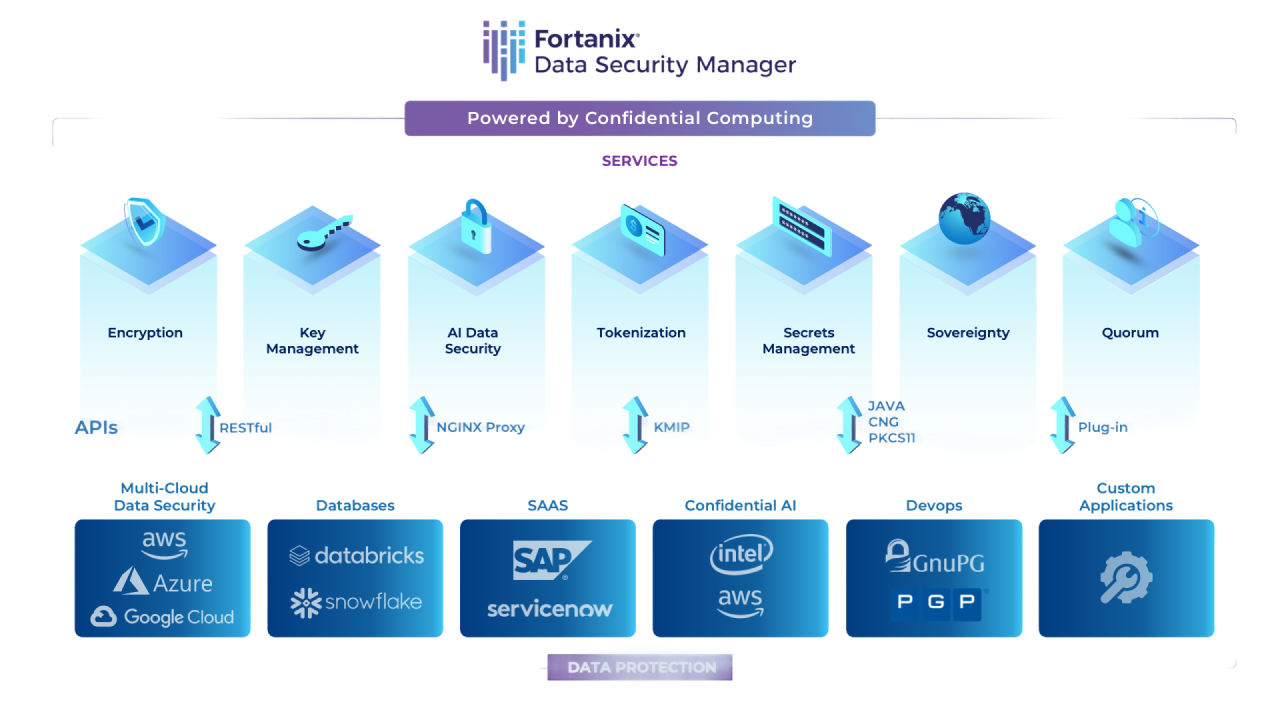
Fortanix Data Security Manager (DSM) is a unified data security platform that delivers a wide range of data security services, including encryption, multicloud key management, and format-preserving encryption, /tokenization, /data masking, TDE, and several others from one single console. It is powered by confidential computing and enables secure generation, storage, and use of cryptographic keys, certificates, and other secrets such as passwords, API keys, or tokens.

Unified Data Protection
Fortanix Data Security Manager delivers HSM, Key Management, Encryption, Tokenization and other security capabilities for your hybrid and cloud-native applications, all from the same integrated solution.

Flexible Deployment
Primarily delivered as a SaaS offering, it also offers other deployment options- on-prem appliance, software, and virtual deployments.

Get Powered by Confidential Computing
With Fortanix Confidential Computing technology powered by Intel® SGX secure enclaves, data always remains secure across its lifecycle- at-rest, in-transit, and in-use.in-use.

Rest API-Driven Architecture
Powerful RESTful APIs make it easy for developers and DevOps teams to use and integrate data security into their applications.

Suited for Any IT Infrastructure
The platform secures data across your IT infrastructure including all cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP), databases (Oracle, SAP HANA, SQL, Server, and more) and applications like ServiceNow, Snowflake, Salesforce etc.
State-of-the-Art Data Security
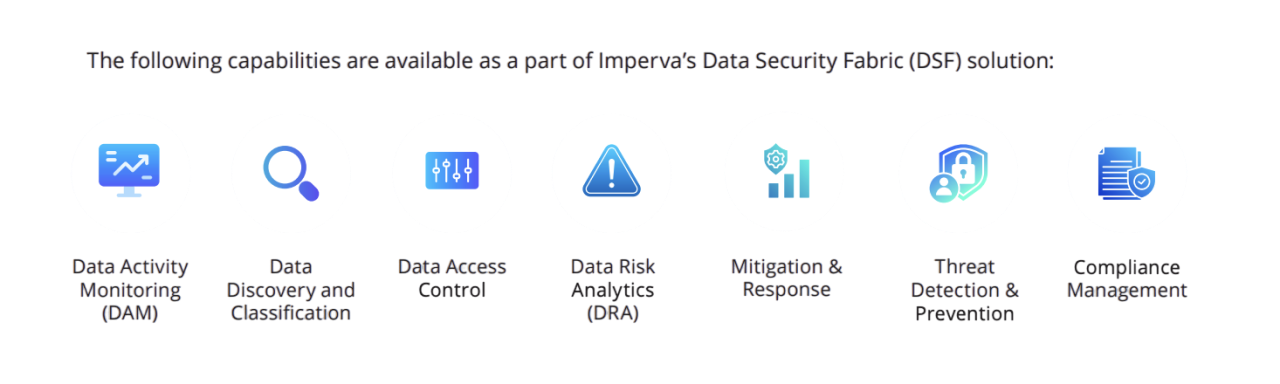
The Imperva Data Security Fabric (DSF) uses a combination of data science, machine learning, and behavior analytics to provide real-time protection for data repositories against internal and external threats, monitor user activity while alerting data security teams of suspicious behavior that exceeds the normal user behavior baseline. Data Security teams can utilize the Imperva DSF dashboard to provide visibility into suspicious behavior, where sensitive data resides, who is accessing it, if sensitive data is protected with the proper controls, automated risk and compliance reporting, as well as explanations to assist them, so they can quickly analyze the situation and respond to them.
Fortanix Data Security Manager