Content
Data Tokenization
What is Data Tokenization?
Data Tokenization is a format-preserving, reversible data masking technique useful for de-identifying sensitive data (such as PII) at-rest. As data tokenization preserves data formats, the de-identified data can be stored as-is in data stores.
Applications that do not require the original value can use the tokenized value as-is; applications authorized to access the original value can retrieve the original value from the token for further use.
Why should I care about Tokenization?
Tokenizing your data early, during data generation or ingestion, removes the risk of exposing sensitive data if a data breach occurs. This significantly reduces the reputational risk and remediation cost, as the data contains no sensitive or PII information.
Tokenization is useful to maintain compliance with ever-increasing data privacy regulations such as GDPR, Schrems II, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Tokenization also enables you to share data seamlessly with 3rd parties and across geographies.
What are the various methods of tokenization?
There are two approaches for tokenization: Vaulted and Vaultless.
Vaulted tokenization generates a token in the same format as the original. It stores the mapping between the original value (in encrypted form) and its token in a secondary database for reversibility. This enables retrieval of the original value.
However, due to the secondary database, the vaulted approach has performance and scalability drawbacks with increasing data volume. Further, the secondary database incurs additional infrastructure and management costs.
Vaultless tokenization, the current state-of-the-art, uses a format-preserving encryption (FPE) algorithm with a symmetric key to tokenize data. Detokenization is simply a decryption operation performed with the same symmetric key. Two FPE algorithms, AES FF1, and FF3-1, are currently approved by NIST. FF1 is considered more mature and has greater adoption than FF3-1.
Fortanix supports Vaultless tokenization using the NIST-standard FF1 algorithm.
What is the advantage of Tokenization over Database encryption?
Tokenization is format-preserving and portable. This means that data can be tokenized (encrypted with FF1) once upon generation or ingestion and then be copied internally or shared externally as needed.
Most applications that do not need access to sensitive fields can use the tokenized data as-is. However, the small set of applications that might need access to sensitive fields can decrypt the tokenized data on the fly to obtain the original values.
As database encryption is not format-preserving, such data must be decrypted and masked on each read operation. Further, you will need to decrypt and re-encrypt data as it moves from one data store to the next: from a transactional database to an analytical database.
Tokenization requires some upfront low-code development in the application or in an ETL pipeline node to tokenize the data. Still, the low initial effort provides greater ongoing benefits than database encryption.
What is the optimal point in the data lifecycle to tokenize sensitive data?
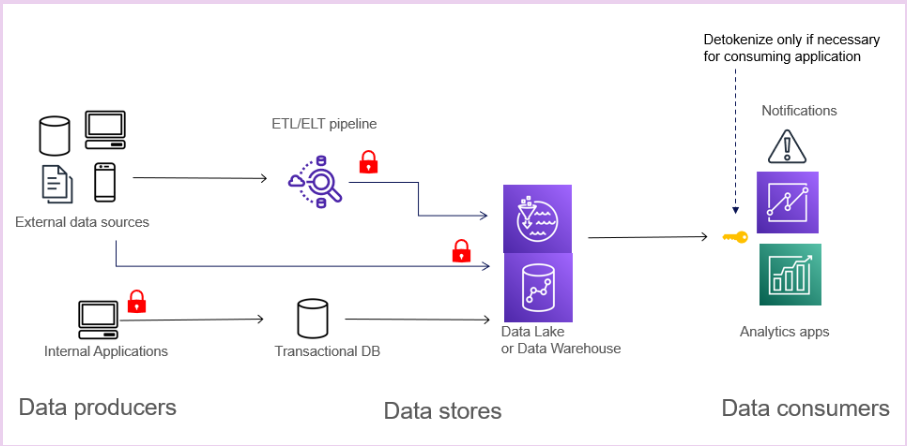
Perform tokenization early, ideally at the data generation or data ingestion stage. Tokenizing in the generating application provides the highest security and performance. However, this can be difficult to govern compliance as the number of applications increases. Tokenization performed in the ETL/ELT pipeline during streaming or batch ingestion performs well and is easy to control for compliance. It can be implemented without having to update the data-generating applications.
Another option is to tokenize at the time of data store writes with User Defined Functions supported by the data store. This is a transparent approach and easy to govern; however, it may impact performance for low-latency transactional databases.
What is Card Tokenization?
Tokenization protects sensitive payment information like credit and debit card details. It involves replacing the original sensitive data, such as the 16-digit card number, cardholder name, expiration date, and security code, with a unique substitute known as a "token."
The cardholder data is transformed into a series of random numbers with no meaningful correlation to the original information. This makes the tokenized data meaningless to anyone who might gain unauthorized access. Tokenization operates similarly to encryption, which converts data into an unreadable form, but with one key distinction: tokenization is irreversible. Once data is tokenized, it cannot be converted back to its original form.
Tokenization is especially useful when sensitive data needs to be stored, like recurring payments or merchant-initiated transactions. It is used to speed up the checkout process by allowing merchants to retain a token for a customer's card, reducing the need for customers to input their information every time they make a purchase.
One of the significant advantages of tokenization is its compliance with security standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Tokenized credit card data can be stored within an organization's secure environment without violating these standards.
Because tokenization maintains the original format and length of the data, businesses can continue using the tokenized data in their existing processes without significant disruptions.
The security benefits of tokenization are clear: it adds an extra layer of protection for consumers' card information because the merchant does not retain the card details. While tokenization is not obligatory, it is highly recommended as a essential service to safeguard consumer data during payment transactions.
How does card tokenization work?
The process involves several steps to ensure security and usability:
Data Collection: At stage 1, a customer fills in the details of their payment card, and the merchant collects this sensitive data, including the 16-digit card number, cardholder name, expiration date, and security code (CVV/CVC).
Token Generation: The collected card data is then forwarded to a tokenization service provided by a trusted third party or managed by the merchant's payment gateway. This service generates a token that is unique to that specific card data.
Token Storage: The token is then stored in the merchant's system or database. At the same time, the original sensitive card data is immediately discarded or stored in a highly secure, compliant-friendly system.
Transmission: The token is returned to the merchant and can be used for future transactions. If unauthorized users gain access to the database, they cannot reverse-engineer the original card data from the token.
Transactions: The merchant uses the token instead of the card data for subsequent transactions. The token is sent through the payment process like the original card data.
Authorization: The payment processor or payment gateway receives the token and uses it to request authorization from the card issuer. When the card issuer recognizes the token, the payment processor processes the transaction as the actual card data.
Decryption and Payment: The payment network decrypts the token and uses the original card data to complete the transaction. The merchant receives payment approval without direct access to the real card details.
How does tokenization make online payments more secure?
Here's how tokenization makes online payments more secure compared to using your credit card directly:
Data Exposure:
Credit Card: There's a risk that the number, expiration date, and CVV can be exposed to the merchant. This data can be stored insecurely and intercepted during transmission, leading to potential breaches.
Tokenization: It replaces sensitive card data with a random token, and the actual card information is not transmitted or stored, significantly reducing the risk of data exposure.
Randomization:
Credit Card: A credit card number follows a predictable pattern based on the card issuer. Attackers can exploit this predictability and can guess the card numbers.
Tokenization: Tokens are random and have no inherent pattern, which makes it extremely difficult for attackers to guess or reverse-engineer the original data from the token.
Dynamic Tokens:
Credit Card: Unauthorized users can misuse card data for payment transactions because authorization is not required.
Tokenization: Dynamic tokens are valid only for specific transactions or within limited time frames. This prevents unauthorized reuse of intercepted tokens.
Centralized Security:
Credit Card: When merchants manage credit card data directly, it can lead to varying levels of protection that are not up to regulatory standards.
Tokenization: Payment processors or dedicated tokenization services offer centralized security expertise, potentially offering higher levels of protection.
Compliance:
Credit Card: Merchants cannot comply with strict PCI DSS compliance standards when storing actual credit card data
Tokenization: Since actual cardholder data is not stored, it meets the requirements of all compliances.
What is network tokenization?
Network tokenization is a payment security approach provided by networks like Mastercard, Visa, American Express, Maestro, Rupay, Union Pay, Discover, etc. It replaces sensitive card data like primary account numbers (PANs) with unique tokens to enhance security during transactions.
The card brands generate these tokens and constantly update them. Even if a physical debit or credit card is locked due to suspected fraud, the network token ensures that the user's payment credentials remain up to date in real time. As a result, customers encounter fewer instances where transactions are declined due to outdated information. This supports user satisfaction during recurring transactions. Merchants get increased security, reduced declines, cost savings, and improved checkout experiences.
Unlike PCI tokenization, which replaces PANs at specific points, network tokenization affects the entire payment process. Network tokens are domain-specific and tied to a single device, merchant, channel, or transaction type. This means they are limited to specific devices, merchants, channels, or types of transactions.
What is data tokenization in banking?
Data tokenization in banking means replacing sensitive data, such as a credit card or account numbers, with a random string of characters called a token. This token has no meaningful value on its own, but it links back to the original data in a secure system. If someone steals the token, it’s useless without access to the secure system that maps it back to the real information.
Banks use data tokenization to protect customer data (PII) during online or mobile payment transactions. This lowers the risk of data theft because real data isn’t exposed or stored in systems where it could be stolen.
What is tokenization in blockchain?
Data Tokenization in blockchain means turning money, real estate, artwork, or company shares into digital tokens stored and traded on a blockchain. Each token represents ownership or rights to that asset.
For example, a $1 million property can be broken into 1,000 tokens worth $1,000 each. Users can buy, sell, or transfer tokens without approaching traditional broker chains. Since all transactions are recorded on a blockchain, they are transparent and hard to tamper with.
This method facilitates faster trading, avoids middlemen, and opens up access to assets that are usually hard to divide or sell.
What is data tokenization in data science?
Data tokenization in data science helps simplify text and make it readable for machines. It breaks words, but sometimes characters or subwords into smaller pieces called tokens so that computers can understand and work with language data.
It’s one of the first steps in natural language processing to turn raw text into a structured form that models and algorithms can handle. For example, the sentence “Alps are beautiful” would be tokenized into three parts: “Alps”, “are”, “beautiful”. The structured parts help the machines for further analysis, translation, or training a machine learning model.
What is Format Preserving Data Tokenization?
Format Preserving Data Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens while maintaining exact format, length, and data type characteristics—a 16-digit credit card becomes a different 16-digit number.
Format Preserving Encryption (FPE) using cryptographic algorithms like FF1 or FF3-1 that mathematically transform data without requiring a separate vault, or vault-based systems that generate format-compliant random tokens and store mappings in secure databases.
How does API data tokenization work?
API data tokenization replaces usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers with a non-sensitive token before the data is sent through an API. The token acts as a stand-in. It can be used for identification or access, but it has no real meaning if someone intercepts it.
The real data either stays secure in a protected system, called a vault or in Format-preserving encryption, which transforms real data into ciphertext within the same format, ensuring compatibility with existing data structures and applications.
When needed, the system maps the token back to the original value. Apps and services can work with
How to meet data tokenization PCI compliance requirements?
Data tokenization can reduce the burden of PCI DSS compliance—if it’s done correctly. Below are the key areas you need to get right.
1. Use Strong, Non-Reversible Tokens
The token should not resemble the original card number in any way. It needs to be random and meaningless outside your system. If someone steals it, they shouldn’t be able to reverse it or figure out the real data behind it.
2. Store Card Data in a Secure Vault or Use Format-Preserving Encryption
The actual card information (PAN, CVV, etc.) should be kept in a secure environment—either protected in a vault with encryption, access controls, and monitoring, or secured through format-preserving encryption using cryptographic keys. With vault-based tokenization, the vault is the only place where the token can be linked back to the original data, while format-preserving encryption enables direct mathematical reversal using proper encryption keys without requiring separate storage.
3. Control Who Has Access
Limit access to both the token vault and any systems that request the original data. Access should be restricted to specific roles and logged thoroughly. This reduces risk and helps during audits.
4. Reduce PCI Scope Through Segmentation
If your main systems only handle tokens and never touch raw card data, you can remove those systems from PCI DSS scope. But this only works if your data tokenization process is solid and well-documented.
5. Monitor and Audit Token Activity
Set up alerts and logs for any activity involving tokens or access to the vault. Regular reviews can catch misuse early and are often required during compliance checks.
6. Work With PCI-Compliant Vendors
If you’re using a third-party data tokenization provider, make sure they can prove their PCI DSS compliance. Don’t just take their word for it—ask for documentation and certifications.
How does data tokenization protect payment card data in transit?
When payment card data moves from one system to another such as a customer’s phone to a payment processor, it is exposed to interception or theft risks. Data tokenization helps reduce that risk by replacing the real card number with a token before the data is sent. That token has no real value if someone steals it during transmission.
When a transaction starts, the system immediately converts the card number into a token using a secure process. This token is sent through the network instead of the card data. Even if someone manages to intercept the message, all they get is a string of random characters that can’t be traced back to a real card.
The real card data stays protected through format-preserving encryption or secure vaults that never travel across networks. Only trusted systems with the right encryption keys or vault permissions can map a token back to the real data, and only when it's needed. Data tokenization keeps sensitive card information out of reach during every transaction step, whether using cryptographic transformation or vault-based storage.
What are the benefits from data tokenization in data cleaning?
Data tokenization helps clean text by splitting it into smaller pieces, usually words. This makes it easier to remove punctuation, extra spaces, or common words that don’t add meaning (such as “the” or “and”). Once the text is broken down into tokens, you can make everything lowercase or fix spelling, which is harder to do with large blocks of unstructured text.
It also helps you spot patterns and problems in your data. For example, you can find repeated phrases, missing words, or unusual terms more easily when the text is already in token form. Tokenized text is also what most machine learning tools expect as input, so cleaning it this way makes your data ready for analysis.
Why is there data tokenization in data mining?
Data tokenization in data mining helps prepare text data for analysis. Raw text, such as reviews, emails, or social media posts, is unstructured and hard for machines to understand. When they are broken into tokens (words or phrases), you structure that data. This makes it possible to search, count, compare, and find patterns across large amounts of text.
Once text is tokenized, it becomes possible to apply models that detect patterns, group similar documents, find frequent terms, or predict outcomes. For example, if you want to find out what customers are saying about a product, data tokenization helps you pull out the important words and ignore the noise.
You can build models to identify spam, track customer sentiment, or group feedback into topics. It’s also the first step in keyword analysis, topic modeling, or detecting sentiment. Without data tokenization, most text data is too messy to mine for insights.
What is the difference between data masking and data tokenization?
Data masking permanently alters or obscures sensitive data by replacing it with fictional but realistic-looking values. For example, a masked credit card number might look like 4567-XXXX-XXXX-1234. It keeps the format but scrambles the content. The original data cannot be recovered from masked data - it's a one-way transformation designed for non-production environments like testing, development, or analytics.
Data tokenization, on the other hand, replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholder tokens that can be mapped back to the original data when needed. For example, the credit card number might become "tok_abc123xyz" or, with format-preserving tokenization, "8732-9456-2847-1093." Crucially, tokenization is reversible - authorized systems can retrieve the original data using proper keys or vault access.
| Feature | Data Masking | Data Tokenization |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hide real data for testing, training, or internal use | Replace sensitive data for security and compliance |
| Output | May or may not preserve format | Random string, unrelated to original data, maintains exact format for system compatibility |
| Reversibility | Usually irreversible | Reversible when authorized |
| Use Case | Development, QA, analytics without exposing real data | Secure payment processing, PCI compliance |
| Data Storage | Masked data remains in the system | Real data is stored separately in a secure vault |
| Security Level | Masking eliminates risk by destroying sensitive data | Tokenization transfers risk to secure key or vault management |
| Example | 4567-XXXX-XXXX-1234 | TKN-abcd1234xyz or 8732-9456-2847-1093 |
| Regulatory Use | Often used for non-production environments | Used in live systems to reduce PCI DSS scope |
What is card-on-file data tokenization?
Card-on-file data tokenization replaces a saved payment card number with a token when a business stores customer payment details for future use. Instead of keeping the actual card number (PAN), the system stores a token that links to the real card in a secure vault.
E-commerce sites, subscription services, and mobile apps commonly use this. It protects cardholder data from theft, since the token is useless without access to the secure system that holds the card information. Even if a system storing the token gets breached, no real card data is exposed.
Card-on-file data tokenization also helps reduce PCI DSS compliance burden because the business doesn’t store actual card numbers, which are considered sensitive.
How does data tokenization make online payments more secure than using your credit card?
Sensitive data such as the card number and CVV can be intercepted or stolen in an online transaction if the system isn’t fully secure. Data tokenization prevents that risk by replacing your card data with a random token before it leaves your device or enters the merchant’s system.
This token acts like a stand-in. It can be used for the transaction, but it has no value on its own. Even if hackers steal it, they can't turn it back into your card number without the proper encryption keys or vault access.
The real card data is kept safe through format-preserving encryption or in a secure vault, separate from the payment system. So instead of sharing actual card details across networks and storing them in databases, data tokenization keeps them hidden, making it much harder for attackers to steal financial information.









