Introduction
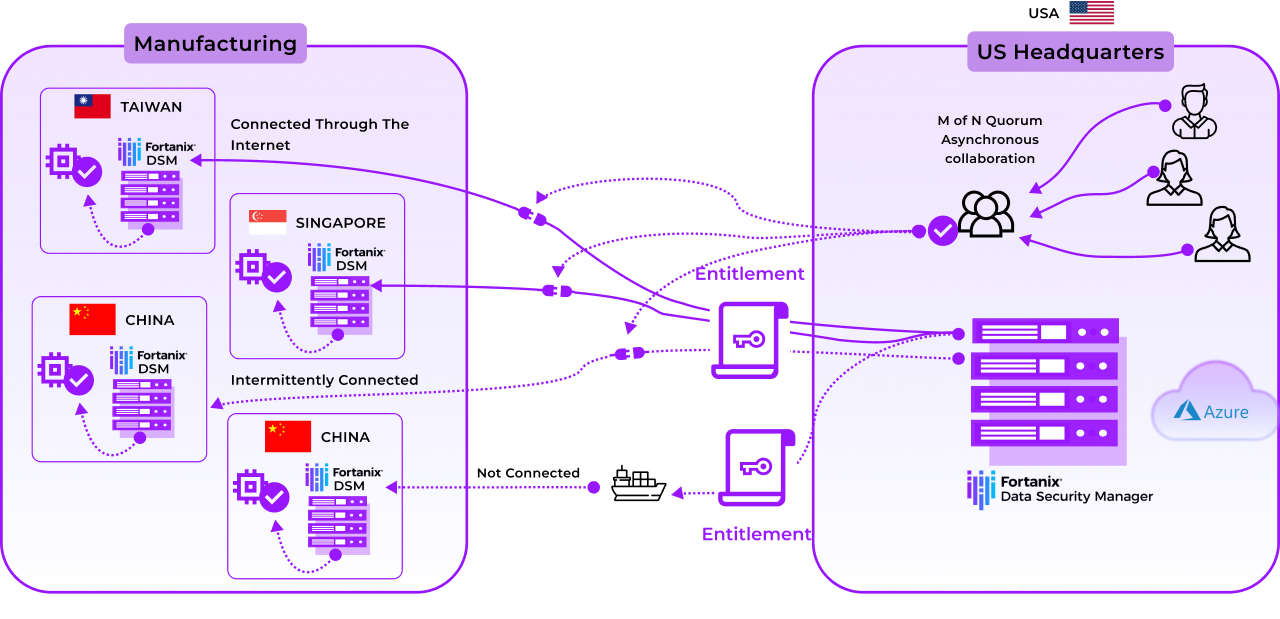
Device manufacturers face a growing threat from counterfeit devices, which have the potential for severe financial and brand reputation damage. These devices are typically manufactured in remote sites that may not have the same level of security as the company headquarter.
Organizations have traditionally addressed this problem by injecting cryptographic keys into devices during manufacturing. However, managing this injection process in today’s cloud-centric and geographic-disparate world requires a new solution.
Fortanix Data Security Manager delivers a scalable cloud-native solution for an end-to-end management of the manufacturing process across global sites, including those not connected to Internet.
Secure Manufacturing using Fortanix Data Security Manager
Fortanix Data Security Manager is the ideal solution for secure manufacturing. It is secure, reliable, highly available, and horizontally scalable. The Runtime Encryption Plugin feature in Fortanix Data Security Manager allows custom code to be run in a trusted execution environment. This allows policies for usage and access control of keys to be defined and enforced by a device manufacturer across multiple sites.
An IoT device manufacturer typically deploys a Fortanix DSM KMS cluster at the headquarters, and a Fortanix DSM cluster at each manufacturing site. Each of these clusters contains a certificate issued by a common root CA, which allows the site clusters to trust the cluster at the headquarters. There is no network connection between the Fortanix Data Security Manager clusters at the two sites.
The following are the sequence of events in the secure manufacturing process:
- The device manufacturer creates a Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster at its headquarters (called "Fortanix Data Security Manager HQ”). Another Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster is created at the manufacturing site (called “Fortanix Data Security Manager Site”). The processing at both ends is done within Runtime Encryption plugins — an “Entitlement Plugin” at Fortanix Data Security Manager HQ, and a “Device Key Plugin” at Fortanix Data Security Manager Site.
- Entitlement Plugin generates a set of keys and associated policy for usage of those keys, and then creates a package with this information. The Entitlement Plugin then encrypts the package with the public key of the Device Key Plugin. The encrypted package is finally signed with its private key to create the final entitlement. This entitlement is then transmitted to Fortanix Data Security Manager site.
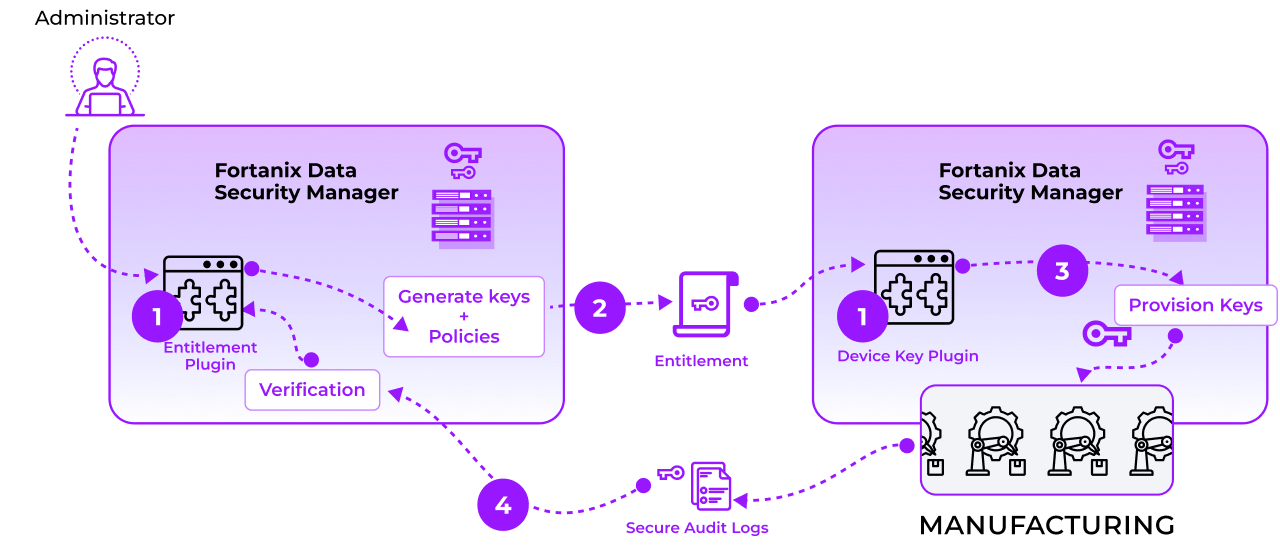
- The Device Key Plugin at Fortanix Data Security Manager Site receives the entitlement. It first verifies that the entitlement is signed by a plugin it can trust. This is ensured by the PKI infrastructure in place which issues certificates for Fortanix Data Security Manager HQ and Fortanix Data Security Manager Site. Then it uses its private key to decrypt the entitlement. The plugin then launches the process for provisioning the keys according to the policy specified in the entitlement. During the process, the plugin logs its activities. This audit log is then encrypted using the public key of the Entitlement Plugin and signed using the private key of the Device Key Plugin. The signed and encrypted audit log is then sent back to Fortanix Data Security Manager HQ.
- The Entitlement plugin receives the signed and encrypted audit logs. It verifies that the logs have been signed by a Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster that it can trust, and then decrypts the logs. The plugin then analyzes the decrypted logs to verify that the policy of key usage has been enforced at the manufacturing site.
Security, Scalability, and Reliability
The secure manufacturing process using Fortanix Data Security Manager addresses security in the following ways:

The keys to be provisioned in the devices are always kept encrypted - when stored at rest, when being transmitted between Fortanix Data Security Manager clusters, and also when being used. The Runtime Encryption plugins that handle the keys are run inside Intel SGX enclaves which protect the confidentiality and integrity of these keys.

Policies for key usage are generated, transmitted, and enforced inside Intel SGX enclaves, which ensures the confidentiality and integrity of these policies.

Every plugin is issued a certificate which is chained to the certificate of the Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster. The Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster certificate in turn is issued by the root CA of the manufacturing company. This chain of trust is used by plugins to trust each other.

Plugins use public key infrastructure to securely transmit data between plugins. Every plugin is instantiated with an asymmetric key pair which is regenerated when the plugin gets updated. Plugins can then use this to encrypt data which only a specified plugin can decrypt. We use this to encrypt entitlement which is sent to Fortanix Data Security Manager Site, and the audit logs which are sent back to Fortanix Data Security Manager HQ.
In addition to security, Fortanix Data Security Manager provides significant flexibility to manufactures in terms of how to specify policies. Policies may be specified in the form of code, and run within Runtime Encryption plugins, which provides a mechanism to run custom code inside Intel SGX enclave. Policies may include daily limits on the number of devices that may be manufactured, time limits for usage of keys, or requirement for quorum approval before a key may be used.
Fortanix Data Security Manager also addresses the problem of scale and reliability, which are often considered limitations of traditional HSM solutions. A Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster provides horizontal scalability and can easily respond to a surge in demand. A standard Fortanix Data Security Manager cluster supports high availability and is resistant to a high number of node failures. If Fortanix Data Security Manager Site has 3 or more nodes, the cluster remains available even when a node fails, and the tolerance to such faults increases with greater number of nodes in the cluster.











