The root cause of data breaches can be stolen credentials, misconfigurations, malware or exposed encryption keys. If an organization loses control of encryption keys, the strongest encryption becomes useless.
That’s why two questions matter the most:
- How do we lock the key vaults?
- How do we control who gets the key?
Cloud HSM (Hardware Security Module) and KMS (Key Management Service) manage these queries from different sides. One keeps the keys sealed in hardware, and the other governs their use with precision. When combined, they ensure that every key is tracked, accounted for, and impossible to copy in secret.
The Two Sides of Key Protection
The data organizations protect is exposed if the keys are stolen or misused.
Here’s how the two solutions work separately:
| Technology | Purpose | Strengths | Limitations Alone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud HSM | Stores and processes cryptographic keys inside tamper-proof hardware in the cloud. | Hardware-grade protection, meets strict compliance standards, and is resistant to physical and software attacks. | Limited central visibility and lifecycle control. |
| KMS | Manages who can create, use, rotate, or revoke encryption keys. | Centralized policy enforcement, integration with apps, and automation. | Relies on software-based storage unless backed by HSM. |
Individually, each is strong. Together, they’re formidable.
Why the Cloud HSM and KMS Combination Matters
As businesses move more workloads to the cloud, encryption keys need to be protected and managed across different platforms—public clouds, SaaS services, and on-prem systems. Cloud HSM and KMS together make this possible with strong physical security and centralized control.
1. Hardware Security + Policy Control
A Cloud HSM keeps keys inside tamper-proof hardware that cannot be extracted, even by the cloud provider. Every request to use a key is routed through the KMS, which checks permissions, logs the activity, and enforces policies. A stolen credential or compromised account still can’t use the key without passing your defined rules.
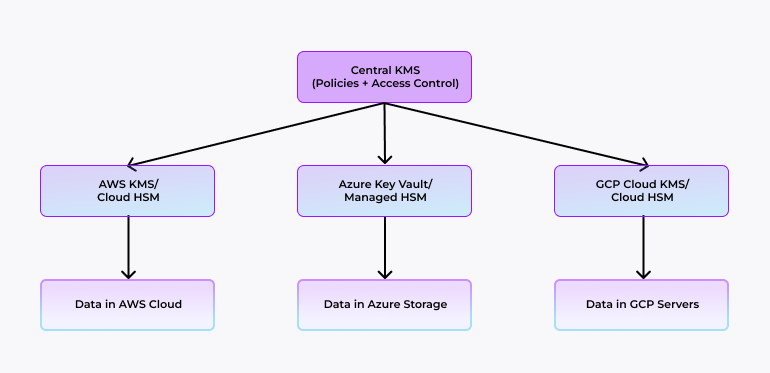
2. Consistency Across Clouds
In a multi-cloud setup, AWS, Azure, and GCP each have separate key management tools, formats, and limits, which can create security gaps and administrative complexity.
| Provider | Native Key Tool | Limitations Without Central Control |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | AWS KMS / CloudHSM | Policies managed separately, limited to AWS services |
| Azure | Azure Key Vault / Managed HSM | Different policy syntax, limited interoperability |
| GCP | Cloud KMS / Cloud HSM | Separate API structure, no unified key lifecycle view |
A combined HSM + KMS approach applies a single set of policies and procedures across all platforms, so the same security standard follows the data wherever it goes.
3. Instant Incident Response
When a breach is suspected, speed matters. With HSM-backed keys managed by a KMS, you can revoke, disable, or destroy a key immediately without touching the hardware or logging into each cloud provider’s console. This rapid action reduces the window of exposure and helps contain the incident.
How Cloud HSM and KMS Improve Business Efficiency
| Benefits | Impact |
|---|---|
| Keys never leave hardware; strong isolation. | Minimizes potential breach costs, protects brand reputation, and reduces legal exposure. |
| Meets FIPS, GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS requirements | Shortens audit cycles, lowers compliance overhead, and avoids regulatory penalties. |
| Automate key rotation and provisioning | Speeds up project timelines, reduces operational bottlenecks, and cuts labor costs. |
| BYOK and multi-cloud consistency | Avoids vendor lock-in, enables multi-cloud strategy, and supports rapid workload migration. |
| Immediate revocation and destruction | Limits downtime, reduces data loss, and lowers recovery and remediation expenses. |
- Keys never leave hardware; strong isolation.
Encryption keys locked inside secure hardware reduce the likelihood of a security incident. This prevents costly breach investigations, avoids loss of customer trust, and keeps the business operating without the disruptions that often follow a data compromise. - Meets compliance requirements
Audit cycles become shorter and less resource-intensive when systems align with established regulatory standards. This means fewer hours spent on compliance preparation, faster approvals, and more time for teams to focus on revenue-generating activities instead of paperwork and back-and-forth with auditors. - Automated key rotation and provisioning
Automating routine security tasks removes human delays and manual intervention in repetitive processes. This speeds up project delivery, reduces staffing costs, avoids the potential for human error, and allows skilled personnel to dedicate their time to strategic work that directly contributes to business growth. - BYOK and multi-cloud consistency
Using the same encryption keys across multiple cloud providers gives the business the flexibility to move workloads quickly when costs, performance, or strategic priorities shift. This avoids being locked into a single vendor’s pricing or timelines, allowing the organization to adapt faster and cost-effectively to market demands. - Immediate revocation and destruction
When compromised keys can be revoked instantly, potential damage is contained before it affects wider operations. This reduces downtime, protects revenue from prolonged service interruptions, and lowers the cost and complexity of recovery after a security event.
More read on: Long Live Hardware Security Module (HSM)
Why combining Cloud HSM and KMS matters now
Multi-cloud growth means data is scattered across different providers
In a multicloud infrastructure, data becomes fragmented across different environments. Because each environment has its own protocols, applying consistent protection for encryption keys is difficult, increasing the risk of security gaps. Without centralized key management, teams waste valuable time duplicating processes and troubleshooting mismatches between providers. Using Cloud HSM and KMS together creates a consistent framework that simplifies control and reduces operational risk.
Ransomware attacks increasingly target encryption keys
Modern ransomware aims to compromise encryption keys rather than encrypt data, allowing attackers to control access or decrypt information without detection. Such attacks can cause extended downtime, significant recovery costs, and severe reputational harm. Organizations dramatically lower the chance of key compromise by storing keys in secure hardware and managing them with automated lifecycle controls. This combination safeguards operations, protects revenue, and controls recovery costs.
Auditors want proof of both technical and procedural controls
Regulators now demand more than written policies; they expect demonstrable evidence that encryption keys are protected by both technology and process. Without this proof, certifications can be delayed, penalties imposed, and projects slowed. Cloud HSM and KMS provide detailed logs, enforce strict controls, and automate compliance reporting, which satisfies auditors efficiently. This reduces the time and resources spent on audits and allows teams to focus on core business priorities.
Distributed teams mean more entry points and more need for policy-driven access
Critical system access points increase dramatically as teams work from multiple locations and devices. Each access point can be a vulnerability if not managed, creating additional operational risk. Manually granting and revoking permissions is slow, error-prone, and costly. Policy-driven, centralized key access through HSM and KMS ensures secure, role-based access without slowing productivity.
You’ve followed how scattered cloud systems, evolving threats, tighter regulation, and remote teams demand a cleaner, more controllable way to secure encryption keys.
Fortanix answers that need with a unified HSM + key management solution that brings clarity and control back into your hands. If you're curious about how this works in practice and what it could mean for simplifying your security setup, check out the Fortanix Hardware Security Module (HSM) solution brief.











