When it comes to digital business transformation, it’s all about the data. The digital economy is built on the foundation of digital trust. Digital trust relies on protecting sensitive data across its entire lifecycle.
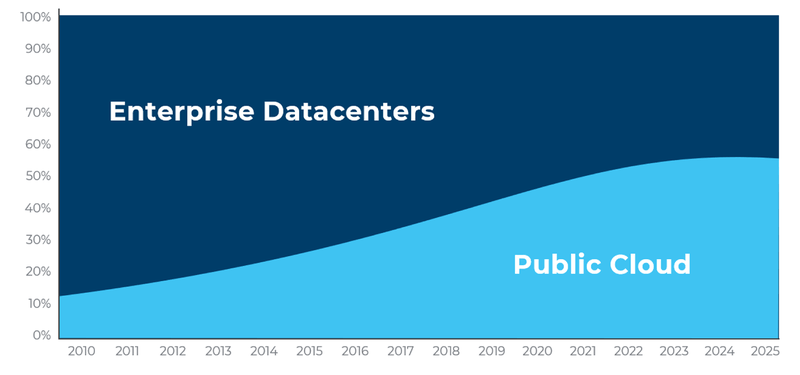
According to IDC, by 2025, more than half of all data will be running in the public cloud. That data will be distributed across the globe with more data in each of the EMEA and Asia Pacific regions than in the United States. This shift introduces new cloud data security challenges that enterprises can no longer ignore.
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), micro-targeted digital advertising, social media, FinTech and big data analytics, much of this data is confidential and sensitive.
Enterprises operating in global markets and businesses relying on public cloud enterprise data centers are concerned about public cloud data security. So, How are we going to protect all this data across its entire lifecycle as it grows exponentially and crosses borders?
To tackle the answer to this challenging question, let’s first start by breaking down the three stages of the data lifecycle:
- Data at Rest – when data is stored on a hard-drive, in the cloud, or in a storage system.
- Data in Transit – when data is moved from one location to another.
- Data in Use – when data is being used by an application and exposed in memory.
The most effective method of protecting data across all three phases of the data lifecycle is encryption. However, while most sensitive data is encrypted while at rest and in transit, almost no data is protected while in use by applications. To secure machine learning workflows, explore how to encrypt Amazon SageMaker notebook data with BYOK.
This is because the data must be decrypted in memory for the application to make use of it. As a result, it is possible for cybercriminals or malicious insiders with access to the infrastructure and applications that handle sensitive data such as payment information, healthcare records and intellectual property to steal that data while it is in use by accessing the memory of the system where the application is running.
Protecting Cloud Applications and Data Using Confidential Computing
According to the Confidential Computing Consortium, the definition of confidential computing is:
“Confidential Computing is the protection of data in use by performing computation in a hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment.”
You might then ask, “What is a Trusted Execution Environments?”. According the IETF TEEP Working Group:
“An environment that enforces that only authorized code can execute with that environment, and that any data used by such code cannot be read or tampered with by any code outside that environment.”
While approaches to TEEs vary, the benefits over conventional cloud computing include:
- Data Integrity
- Data Confidentiality
- Code Integrity
- Code Confidentiality
- Unspoofability and non-repudiation
- Attestability
Confidential Computing is a new and emerging technology that has the potential to dramatically improve the cloud data security posture of in general and enable new types of privacy preserving analytics that weren’t previously feasible. Today, very few cloud workloads use confidential computing but that is about to change.
When it does, cloud data and code will be protected even when the infrastructure is compromised, and an attacker has root access. While not a silver bullet for all security risks, confidential computing is one of the most significant improvements in cloud data security that is on the horizon.
For more information on the characteristics of Confidential Computing, visit the Confidential Computing Consortium github scoping document.
Fortanix and IBM Partner to Protect Data in the Cloud with Confidential Computing
IBM Cloud Data Shield Powered by Fortanix helps businesses move and secure enterprise applications in the public cloud. The service automatically encrypts confidential information at rest, in transit and while in use (confidential computing), while protecting the applications and machine learning algorithms that use this data.
The IBM Cloud Data Shield service provides data protection for financial transactions, healthcare information, and other confidential computing use cases.
Related Read: Fortanix will be showcasing Runtime Encryption at IBM Think
“Confidential computing potentially removes the remaining barrier to cloud adoption for highly regulated businesses or any organization concerned about unauthorized third-party access to data in use in the public cloud, it’s likely that auditors and regulators will demand increased protection of certain data types, including high barriers to provider and government access. Confidential computing enclaves provide such protection now.”
How can you use Confidential Computing?
Confidential Computing is a technology that can be applied to protect data while in use by any enterprise application. In the case of IBM Cloud Data Shield, those applications run in the IBM public cloud.
Using Fortanix Enclave OS, IBM Cloud Data Shield is the only public cloud confidential computing solution that can convert existing applications to run in a secure enclave trusted execution environment (TEEs).
There is also the option to use the open-source Enclave Development Platform (EDP) to write native applications for confidential computing environments.
One exciting new use case for confidential computing is what is called Privacy Preserving Analytics, multi-party analytics or multi-party compute. With the advent of big data, machine learning, and analytics, the ability to share data has the potential to discover drugs that cure diseases, eliminate financial fraud and unlock business insights that transform industries.
However, organizations such as hospitals, financial institutions and businesses are rightfully prohibited by privacy regulations from sharing this powerful data. Advances in encryption, TEEs, and analytics now make it possible to protect privacy while sharing private data, unlocking and advancing new learning.
"Without “singling out” or deidentifying individuals, data can be processed in a controlled, privacy-preserving fashion by applying, for example, secure multiparty computing (SMPC), differential privacy, security or confidential computing “— all in combination with privacy-aware machine learning (PAML) algorithms."
Multiple parties contribute encrypted data to a trusted execution environment called an enclave, where the data is combined, analyzed and then results are output in an encrypted format back to each party with the results of the analytics. Data remains encrypted throughout the entire process, protecting the privacy of the data while it is transferred, during computation and while stored.
Privacy Preserving Analytics in Financial Services
For Financial Services organizations, privacy preserving analytics using confidential computing can be used to perform analytics any time sensitive data needs to be combined and/or analyzed without exposing the underlying data to another party, the infrastructure or even a prohibited geography.
That data could be analyzing transactions to detect money laundering, fraud or the best bank account to offer a mortgage client. The confidential computing technology provides a trusted execution environment that can be used to protect both the data and the code being used to perform that analysis.
Privacy Preserving Analytics in Healthcare
For Healthcare organizations, there are myriad use cases that enable new types of data collaboration to improve disease diagnostics, map a genome, or develop a new drug without exposing private patient data or proprietary intellectual property. For example, a drug company would collaborate with multiple hospitals to use machine learning models to determine the effectiveness of a new drug in trials.
Performing this analysis enables that data to be combined, analyzed and provided back to the drug company and government regulators without anyone seeing the machine learning model used by the drug company or the drug company seeing any patient data.
How Does IBM Cloud Data Shield Work?
IBM Cloud Data Shield provides confidential computing by running containerized applications on IBM Cloud Kubernetes or RedHat OpenShift, both in a secure enclave running on Intel® Software Guard Extension (Intel® Software) hardware.
Customers can use their own custom application without modification and gain the full benefits of the service. In addition, IBM Cloud Data Shield offers pre-configured containers for databases, web servers and OpenStack applications accelerating the secure development of new cloud-native applications.
How does IBM Cloud Data Shield use Fortanix Technology?
The Fortanix Runtime Encryption Platform including the Fortanix EnclaveOS, Confidential Computing Manager and Enclave Development Platform (EDP) are licensed by IBM and provide the foundation of the IBM Cloud Data Shield service, which is offered through IBM cloud.
Enclave Development Platform (EDP) is an open-source project that is generally regarded as the most mature and was ranked as the most secure development environment for creating applications in recent academic research.
When is IBM Cloud Data Shield Available?
As more enterprise workloads move to the cloud, organizations must challenge cloud data security challenges that affect data at rest or in transit, as well as data in use. Confidential computing is the only way to secure sensitive workloads in cloud data security architectures in the public cloud. Fortanix and IBM provide one of the first solutions ready for deployment at scale, making them early movers in solving the cloud data security challenge.
To get started with IBM Cloud Data Shield, start here.
[1] Information sourced from the Confidential Computing Consortium scoping document https://github.com/confidential-computing/governance/blob/master/scoping.md